
Automatic Translation for WordPress
Translate your website instantly and reach a global audience.
Works on WordPress 6.x
Polylang (free version) for WordPress required

Translate your website instantly and reach a global audience.
Works on WordPress 6.x
Polylang (free version) for WordPress required

Translate your WordPress posts in one click without extra translation fees
Automatic translation available in 129 languages covering the entire globe.
No limit on the number of words you can translate.
Translate as many pages and articles as you need.
Translate all your content at once with our powerful bulk translation feature.
Automatically translate new content as soon as it is published.
Automatically translates your categories and taxonomies.
Leverage the power of Google Translate for free.
Connect your Open AI API key for AI-powered content rewriting and translation.
Integrate DeepL API for high-quality neural machine translation.
Fully compatible with WooCommerce products and pages.
Translates custom fields and metadata effortlessly.
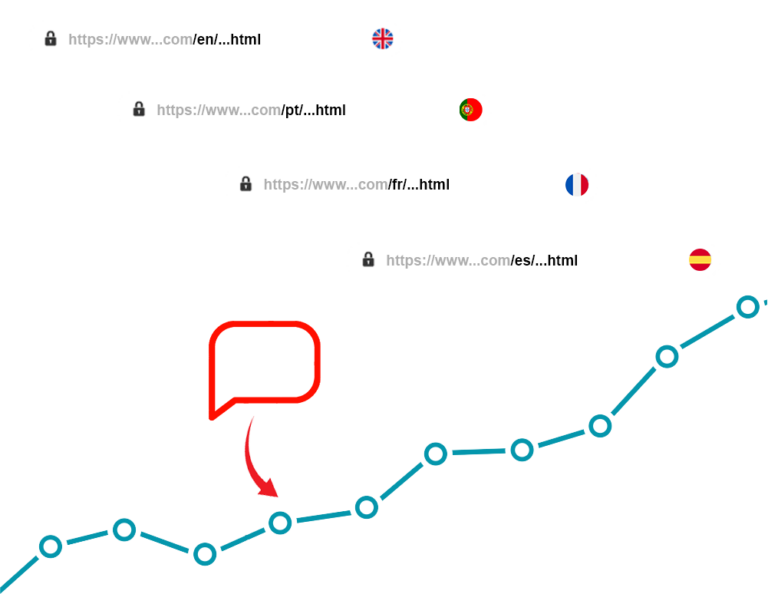
Boost your SEO in a few days! Translating a multilingual website can have significant advantages in terms of search engine optimization (SEO). Reach new markets and increase your organic traffic.

100% FREE
Use the standard Google Translate engine without any API key or cost.
Enter your API key to translate with DeepL's superior neural network.
Add your API key to rewrite and translate your content with AI.
Wptranslation offers a powerful Bulk Translation mode. Imagine the time saved: you can translate thousands of articles in just a few clicks. The Live Automatic mode ensures that every new piece of content you publish is immediately available in all your target languages.
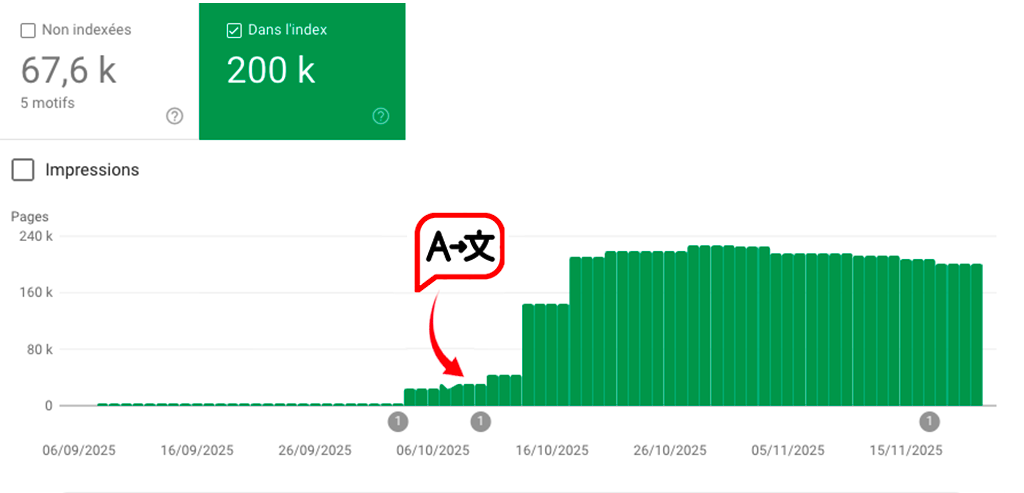
DOWNLOAD"By translating your web pages, you allow users from all over the world to visit your site, significantly increasing your potential audience."
Source: Google Search Console
UNLIMITED WEBSITES
One-time payment. Lifetime license.
No. The Google Translate feature integrated into our plugin uses the public interface, which is completely free to use. You do not need an API key or a paid Google Cloud account.
You need a WordPress installation (version 6.x or newer) and PHP 7.4 or higher. The free version of the Polylang plugin is also required as a base for language management.
The plugin itself has a one-time cost for the lifetime license. The translation service via Google is free. If you choose to use DeepL or OpenAI, you will need your own API keys which may have associated costs depending on your usage with those providers.
The paid version unlocks Bulk Translation (translate all content at once), Live Translation (auto-translate on publish), access to all 129 languages, unlimited words/pages, and priority support.
Yes, Wptranslation is fully compatible with Polylang Pro and WooCommerce. It can translate products, categories, attributes, and other e-commerce related data.